|
|
C++ 异常处理机制:try、catch 和 throw
异常处理是 C++ 中处理运行时错误的机制,通过 分离正常逻辑与错误处理 提升代码可读性和健壮性。
1. 基本结构
异常处理由三个关键字组成:
try:包裹可能抛出异常的代码块。
catch:捕获并处理特定类型的异常。
throw:主动抛出异常对象。
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| try {
// 可能抛出异常的代码
if (error_condition) {
throw exception_object; // 抛出异常
}
} catch (ExceptionType1 &e) {
// 处理 ExceptionType1 类型异常
} catch (ExceptionType2 &e) {
// 处理 ExceptionType2 类型异常
} catch (...) {
// 捕获所有未处理的异常(不推荐滥用)
}
|
2. 异常处理流程
注意:catch(...)捕获所有异常,但无法获取异常信息,通常用于最后兜底。
抛出异常:当throw执行时,程序立即终止当前代码块,开始查找匹配的catch块。
栈展开(Stack Unwinding):
从抛出点开始,逐层退出函数调用栈,直到找到匹配的catch块。
退出时,当前作用域的局部对象会被析构(依赖RAII机制)。
匹配catch块:
catch块按声明顺序匹配异常类型。
若未找到匹配的catch块,调用std::terminate()终止程序。
3. 标准异常类
C++ 标准库定义了一组异常类(需包含 <stdexcept>):
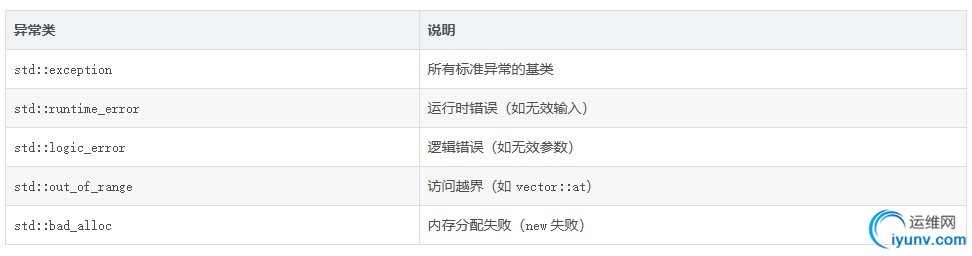
示例:使用标准异常
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <stdexcept>
#include <vector>
void checkIndex(const std::vector<int>& vec, int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= vec.size()) {
throw std::out_of_range("索引越界");
}
}
|
4. 自定义异常类
通过继承 std::exception 定义特定错误类型:
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #include <exception>
#include <string>
class MyException : public std::exception {
public:
MyException(const std::string& msg) : msg_(msg) {}
const char* what() const noexcept override {
return msg_.c_str();
}
private:
std::string msg_;
};
// 使用自定义异常
throw MyException("自定义错误消息");
|
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
| noexcept 关键字
声明函数不抛出异常:
void safe_function() noexcept {
// 保证不会抛出异常
}
|
移动构造函数/析构函数:建议标记为 noexcept,避免容器操作(如 std::vector 扩容)时回退到低效拷贝。
noexcept 运算符:检查表达式是否可能抛出异常。
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
| bool is_noexcept = noexcept(safe_function()); // true
|
5. 捕获异常的最佳实践
按派生类到基类顺序捕获:确保更具体的异常优先处理。
通过引用捕获:避免对象切片(尤其对多态异常类)。
处理已知异常:避免滥用 catch (...)。
优先使用标准异常类:如std::runtime_error,而非基本类型。
按顺序捕获异常:先捕获派生类,再捕获基类。
避免空catch块:至少记录错误信息。
资源管理用RAII:如std::unique_ptr、std::lock_guard。
限制异常使用:仅处理严重错误,避免性能损耗。
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdexcept>
class FileReader {
public:
FileReader(const std::string& filename) : file_(filename) {
if (!file_.is_open()) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
}
// 使用RAII自动关闭文件
~FileReader() noexcept = default;
void read() {
// 读取文件内容(可能抛出异常)
}
private:
std::ifstream file_;
};
int main() {
try {
FileReader reader("nonexistent.txt");
reader.read();
} catch (const std::runtime_error& e) {
std::cerr << "错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "未知错误" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
6. 重新抛出异常
在 catch 块中可重新抛出当前异常(保留原始异常信息):
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
| catch (const std::exception &e) {
std::cerr << "记录错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
throw; // 重新抛出异常,供上层处理
}
|
7. 异常安全(Exception Safety)
确保代码在异常发生时仍保持数据一致性,分三个等级:
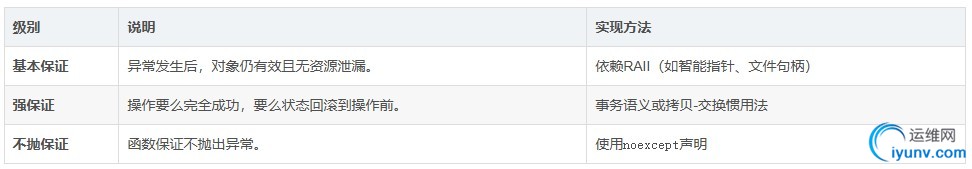
实现强保证的示例:
[C#] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| void updateData() {
auto backup = data_; // 备份原始数据
try {
modifyData(); // 可能抛出异常的操作
} catch (...) {
data_ = backup; // 失败时恢复备份
throw;
}
}
|
8. 异常处理与资源管理(RAII)
通过 资源获取即初始化(RAII) 自动释放资源(如内存、文件句柄),避免异常导致泄漏:
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #include <memory>
#include <fstream>
void processFile(const std::string& filename) {
std::ofstream file(filename); // 文件自动管理
if (!file) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件");
}
// 使用 file 对象,即使抛出异常也会自动关闭文件
}
|
9. 综合示例
[C++] [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]纯文本查看 [color=rgb(51, 102, 153) !important]复制代码
[color=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][color=#ffffff !important]?
运维网代码01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| #include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
class NetworkError : public std::runtime_error {
public:
NetworkError() : std::runtime_error("网络连接失败") {}
};
void connectToServer() {
bool connectionFailed = true;
if (connectionFailed) {
throw NetworkError();
}
}
int main() {
try {
connectToServer();
} catch (const NetworkError &e) {
std::cerr << "错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// 尝试重连或终止程序
} catch (const std::exception &e) {
std::cerr << "其他错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
10. 注意事项
析构函数中的异常:析构函数默认应为 noexcept,若抛出异常可能导致程序终止。
性能开销:异常处理比返回错误码略慢,但现代编译器优化后差异较小。
适用场景:适合处理不可恢复的错误(如文件缺失、内存不足)。
11. 总结

|
|