|
|
1.计数器
计数器是一种收集作业统计的有效手段,用于质量控制或应用级统计。计数器还可以辅助诊断系统故障。
相对于日志,它获取更方便,其次根据计数器值统计特定事件的发生次数要比分析一堆日志文件容易多了。
1)内置计数器
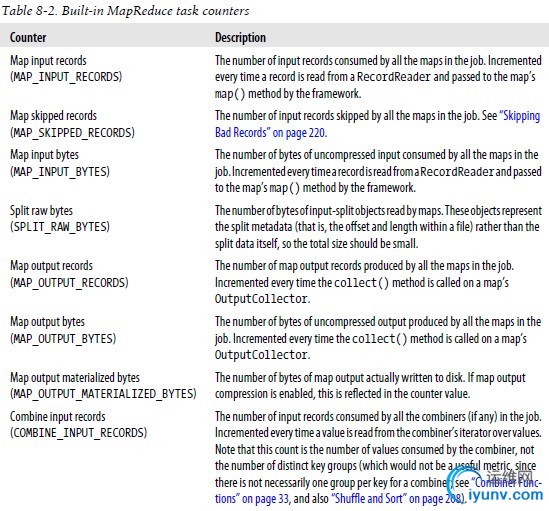
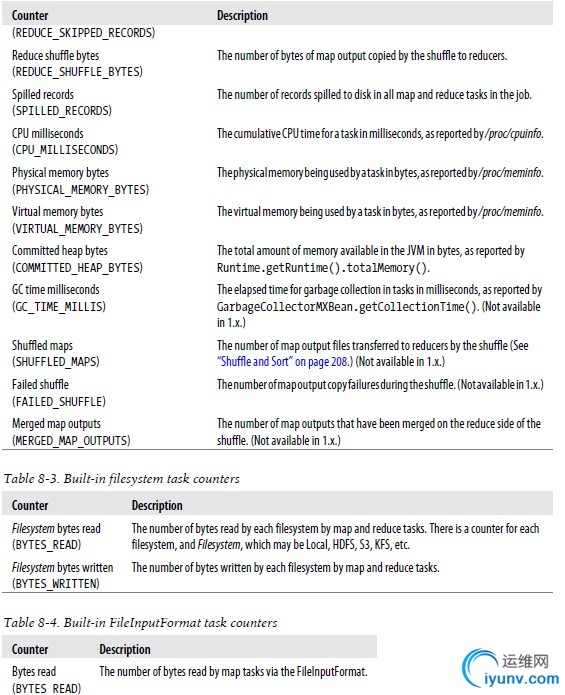
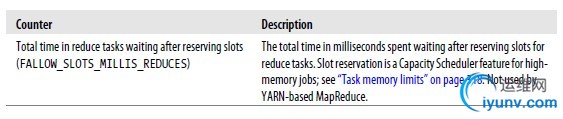
Hadoop为每个作业维护若干内置计数器,以描述该作业的各项指标。
计数器由其关联任务维护,并定期传到TaskTracker,再由TaskTracker传给JobTracker。
与其它计数器不同,内置的作业计数器实际上由JobTracker维护,不必在整个网络中发送。
一个任务的计数器每次都是完整传输的,以避免由于消息丢失而引发的错误。
另外,如果一个任务在作业执行期间失败,则相关计数器值会减小。仅当一个作业执行成功之后,计数器的值才是完整可靠的。
内置计数器分类:

--MapReduce & FS & FileInputForamt
--Job

 2)用户定义的JAVA计数器
2)用户定义的JAVA计数器
MapReduce允许用户编写程序来定义计数器,计时器的值可在mapper和reducer中增加。多个计数器由一个Java枚举(enum)类型来定义,以便对计数器分组。一个作业可以定义的枚举类型数量不限,各个枚举类型所包含的字段数量也不限。枚举类型的名称即为组的名称,枚举类型的字段就是计数器名称。计数器是全局的。换言之,MapReduce将跨越所有mapper和reducer聚集致谢计数器,并在作业结束时产生一个最终结果。e.g.
context.getCounter(RECORD_FORMAT.ERROR).increment(1);
--动态计数器
不由Java枚举类型定义的计数器,程序中直接设置计数器的组名和计数器名称。
实际上它们是等价的,Hadoop需先将Java枚举类型转变成String类型,再通过RPC发送计数器值。
比较:枚举类型易于使用,还提供类型与安全,适合大多数作业使用。
context.getCounter("RECORD_FORMAT", "ERROR").increment(1);
--自定义枚举计数器的名称
枚举计数器的默认名称是枚举类型的Java完全限定类名。可通过资源绑定来修改计数器的名称,并且支持I18N。
以Java枚举类型为名创建一个属性文件,用下划线(_)分隔嵌套类型。属性文件与包含该枚举类型的顶级类放在同一目录。e.g.
MaxTemperatureMapper_RECORD_FORMAT.properties
#group name
CounterGroupName=RECORD FORMAT
#X.name
ERROR.name=BAD FORMAT RECORD
3)获取计数器
--Web界面
--hadoop job -counter指令
--使用Java API,e.g.
MissingTemperatureFields.java
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.*;
public class MissingTemperatureFields extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
JobBuilder.printUsage(this, "<job ID>");
return -1;
}
String jobID = args[0];
JobClient jobClient = new JobClient(new JobConf(getConf()));
RunningJob job = jobClient.getJob(JobID.forName(jobID));
if (job == null) {
System.err.printf("No job with ID %s found.\n", jobID);
return -1;
}
if (!job.isComplete()) {
System.err.printf("Job %s is not complete.\n", jobID);
return -1;
}
Counters counters = job.getCounters();
long missing = counters
.getCounter(MaxTemperatureWithCounters.Temperature.MISSING);
long total = counters.getCounter(Task.Counter.MAP_INPUT_RECORDS);
System.out.printf("Records with missing temperature fields: %.2f%%\n",
100.0 * missing / total);
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new MissingTemperatureFields(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
JAVA API支持在作业运行期间获取计数器的值,但一般都在作业完成,计数器稳定下来时获取。
2.排序
排序是MapReduce的核心技术。尽管应用程序本身可能并不需要对数据排序,但仍可能使用MapReduce的排序功能来组织数据。
1)准备
下面程序将气温对天气数据集排序。我们用顺序文件存储数据,键为气温,值为数据行。
public class SortDataPreprocessor extends Configured implements Tool {
static class CleanerMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Text> {
private NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
parser.parse(value);
if (parser.isValidTemperature()) {
context.write(new IntWritable(parser.getAirTemperature()),
value);
}
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = JobBuilder.parseInputAndOutput(this, getConf(), args);
if (job == null) {
return -1;
}
job.setMapperClass(CleanerMapper.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressionType(job,
CompressionType.BLOCK);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new SortDataPreprocessor(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
2)部分排序
下面程序利用IntWritable键对顺序文件排序
public class SortByTemperatureUsingHashPartitioner extends Configured implements
Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = JobBuilder.parseInputAndOutput(this, getConf(), args);
if (job == null) {
return -1;
}
job.setInputFormatClass(SequenceFileInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressionType(job,
CompressionType.BLOCK);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(
new SortByTemperatureUsingHashPartitioner(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
键的排列顺序控制规则:
--若属性mapred.output.key.comparator.class已经设置,则使用该类的实例。也可调用Job.setSortComparatorClass()方法进行设置。
--否则,键必须是WritableComparable的子类,并使用针对该键类的已登记的comparator。
--如果键没有已登记的comparator,则使用RawComparator将字节流反序列化成一个对象,谈后由WritableComparable的compareTo()方法进行操作。
3)基于分区的MapFile查找技术
输出到MapFile
public class SortByTemperatureToMapFile extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = JobBuilder.parseInputAndOutput(this, getConf(), args);
if (job == null) {
return -1;
}
job.setInputFormatClass(SequenceFileInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(MapFileOutputFormat.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressionType(job,
CompressionType.BLOCK);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new SortByTemperatureToMapFile(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
查找--获取符合指定键的第一项记录
public class LookupRecordByTemperature extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
JobBuilder.printUsage(this, "<path> <key>");
return -1;
}
Path path = new Path(args[0]);
IntWritable key = new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(args[1]));
Reader[] readers = MapFileOutputFormat.getReaders(path, getConf());
Partitioner<IntWritable, Text> partitioner = new HashPartitioner<IntWritable, Text>();
Text val = new Text();
Writable entry = MapFileOutputFormat.getEntry(readers, partitioner,
key, val);
if (entry == null) {
System.err.println("Key not found: " + key);
return -1;
}
NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
parser.parse(val.toString());
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\n", parser.getStationId(), parser.getYear());
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new LookupRecordByTemperature(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
查找--获取包含指定键的所有记录
public class LookupRecordsByTemperature extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
JobBuilder.printUsage(this, "<path> <key>");
return -1;
}
Path path = new Path(args[0]);
IntWritable key = new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(args[1]));
Reader[] readers = MapFileOutputFormat.getReaders(path, getConf());
Partitioner<IntWritable, Text> partitioner = new HashPartitioner<IntWritable, Text>();
Text val = new Text();
Reader reader = readers[partitioner.getPartition(key, val,
readers.length)];
Writable entry = reader.get(key, val);
if (entry == null) {
System.err.println("Key not found: " + key);
return -1;
}
NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
IntWritable nextKey = new IntWritable();
do {
parser.parse(val.toString());
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\n", parser.getStationId(),
parser.getYear());
} while (reader.next(nextKey, val) && key.equals(nextKey));
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new LookupRecordsByTemperature(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
4)全排序
方案一:
只使用一个分区,该方法在处理大型文件时无法利用MapReduce的并行架构优势,效率极低。
方案二:
--创建一系列排好序的文件
--串联这些文件
--生成一个全局排序的文件
主要思路是使用一个partitioner来描述全局排序的输出。
该方案的关键点在于如何划分各个分区。理想情况下,各分区所含记录数应该大致相等,使Job的总运行时间不会受制于个别的reduce。
采样的核心思想是只查一小部分键,获得键的近似分布,并由此构建分区。
InputSampler.Sampler接口
public interface Sampler<K,V> {
//返回一系列样本键
K[] getSample(InputFormat<K,V> inf, Job job)
throws IOException, InterruptedException;
}
getSample方法由InputSampler类的静态方法writePartitionFile调用,目的是创建一个顺序文件来存储定义分区的键。
顺序文件被TotalOrderPartitioner使用,为排序作业创建分区。e.g.
public class SortByTemperatureUsingTotalOrderPartitioner extends Configured
implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = JobBuilder.parseInputAndOutput(this, getConf(), args);
if (job == null) {
return -1;
}
job.setInputFormatClass(SequenceFileInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
SequenceFileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressionType(job,
CompressionType.BLOCK);
job.setPartitionerClass(TotalOrderPartitioner.class);
InputSampler.Sampler<IntWritable, Text> sampler = new InputSampler.RandomSampler<IntWritable, Text>(
0.1, 10000, 10);
InputSampler.writePartitionFile(job, sampler);
// Add to DistributedCache
Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
String partitionFile = TotalOrderPartitioner.getPartitionFile(conf);
URI partitionUri = new URI(partitionFile + "#"
+ TotalOrderPartitioner.DEFAULT_PATH);
DistributedCache.addCacheFile(partitionUri, conf);
DistributedCache.createSymlink(conf);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(
new SortByTemperatureUsingTotalOrderPartitioner(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
RandomSampler:以指定的采样率均匀地从一个数据集中选择样本。
SplitSampler:只采样一个分片中前N条记录,不适合已经排好序的数据。
IntervalSampler:以一定的间隔定期从划分中选择键。
TotalOrderPartitioner类的分区数由用户定义的Reducer数决定。
5)辅助排序
MapReduce框架在记录到达reducer之前按照键对记录排序,但键所对应的值并没有被排序。
有时需要对键进行排序和分组等以实现对值的排序。
--定义包括自然键和自然键的组合键。
--键的comparator根据组合键对记录进行排序,即同时利用自然键和自然键进行排序。
--针对组合键的partitioner和分组comparator在进行分区和分组时均只考虑一个自然键。
public class MaxTemperatureUsingSecondarySort extends Configured implements
Tool {
static class MaxTemperatureMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntPair, NullWritable> {
private NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
parser.parse(value);
if (parser.isValidTemperature()) {
context.write(
new IntPair(parser.getYearInt(), parser
.getAirTemperature()), NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
static class MaxTemperatureReducer extends
Reducer<IntPair, NullWritable, IntPair, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(IntPair key, Iterable<NullWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key, NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static class FirstPartitioner extends
Partitioner<IntPair, NullWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(IntPair key, NullWritable value,
int numPartitions) {
// multiply by 127 to perform some mixing
return Math.abs(key.getFirst() * 127) % numPartitions;
}
}
public static class KeyComparator extends WritableComparator {
protected KeyComparator() {
super(IntPair.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2) {
IntPair ip1 = (IntPair) w1;
IntPair ip2 = (IntPair) w2;
int cmp = IntPair.compare(ip1.getFirst(), ip2.getFirst());
if (cmp != 0) {
return cmp;
}
return -IntPair.compare(ip1.getSecond(), ip2.getSecond()); // reverse
}
}
public static class GroupComparator extends WritableComparator {
protected GroupComparator() {
super(IntPair.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2) {
IntPair ip1 = (IntPair) w1;
IntPair ip2 = (IntPair) w2;
return IntPair.compare(ip1.getFirst(), ip2.getFirst());
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = JobBuilder.parseInputAndOutput(this, getConf(), args);
if (job == null) {
return -1;
}
job.setMapperClass(MaxTemperatureMapper.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(FirstPartitioner.class);
job.setSortComparatorClass(KeyComparator.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupComparator.class);
job.setReducerClass(MaxTemperatureReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntPair.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new MaxTemperatureUsingSecondarySort(),
args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
3.连接
MapReduce能够执行大型数据集间的连接操作,但是考虑到复杂性一般使用更高级的框架,如Pig,Hive或Cascading。
连接操作由mapper执行,则成为“map端连接”;连接操作由reducer执行,则成为“reduce端连接”。
1)map端连接
在两个大规模输入数据集之间的map端连接会在数据达到map函数之前就执行连接操作。
要求:各map的输入数据必须先分区并且以特定方式排序。各个输入数据集被划分成相同数量的分区,并且均按照相同的键(连接键)排序。同一键的所有记录均会放在同一个分区之中。
利用org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.join中的CompositeInputFormat类来运行一个map端连接。CompositeInputFormat类的输入源和连接语法可以通过一个连接表达式来配置,连接表达式的语法较为简单,参考API。
org.apache.hadoop.examples.Join是一个通用的执行map端连接的命令行程序。
2)reduce端连接
reduce端连接并不要求输入数据集符合特定结构,但是由于数据集要经过shuffle过程,所以reduce端连接的效率要低一些。基本思路是mapper为各个记录标记源,并且使用连接key作为map输出key,使key相同的记录放在同一reducer。以下技术能帮助实现reduce端连接
--多输入
--辅助排序
下面几段程序完整的实现了reduce端对气象站的记录进行连接操作,说明:程序中使用TextPair类构建组合key,包括气象站ID和"标记",标记是一个虚拟的字段,目的在于对记录排序,使气象站记录比天气记录先到达,简单的方法是:对于气象站记录"标记"值为0,对于天气记录“标记”值为1
这个mapper类用于reduce端连接中标记气象站的记录
public class JoinStationMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, TextPair, Text> {
private NcdcStationMetadataParser parser = new NcdcStationMetadataParser();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (parser.parse(value)) {
context.write(new TextPair(parser.getStationId(), "0"), new Text(
parser.getStationName()));
}
}
}
这个mapper类用于reduce端连接中标记天气记录
public class JoinRecordMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, TextPair, Text> {
private NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
parser.parse(value);
context.write(new TextPair(parser.getStationId(), "1"), value);
}
}
reducer用于连接已标记的气象站记录和天气记录
public class JoinReducer extends Reducer<TextPair, Text, Text, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(TextPair key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Iterator<Text> iter = values.iterator();
Text stationName = new Text(iter.next());
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Text record = iter.next();
Text outValue = new Text(stationName.toString() + "\t"
+ record.toString());
context.write(key.getFirst(), outValue);
}
}
}
对天气记录和气象站记录名称执行连接操作
public class JoinRecordWithStationName extends Configured implements Tool {
public static class KeyPartitioner extends Partitioner<TextPair, Text> {
@Override
public int getPartition(TextPair key, Text value, int numPartitions) {
return (key.getFirst().hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE)
% numPartitions;
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 3) {
JobBuilder
.printUsage(this, "<ncdc input> <station input> <output>");
return -1;
}
Job job = new Job(getConf(), "Join weather records with station names");
job.setJarByClass(getClass());
Path ncdcInputPath = new Path(args[0]);
Path stationInputPath = new Path(args[1]);
Path outputPath = new Path(args[2]);
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job, ncdcInputPath, TextInputFormat.class,
JoinRecordMapper.class);
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job, stationInputPath,
TextInputFormat.class, JoinStationMapper.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
job.setPartitionerClass(KeyPartitioner.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(TextPair.FirstComparator.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(TextPair.class);
job.setReducerClass(JoinReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new JoinRecordWithStationName(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
4.边数据分布
“边数据”是作业所需的额外的只读数据,以辅助处理主数据集。挑战在于如何使所有map或reduce任务都能方便高效地使用边数据。
1)利用JobConf配置文件
2)分布式缓存
在任务运行过程中及时地将文件和存档复制到任务节点以供使用。为了节约网络带宽,在每一个作业中,各个文件通常只需要复制到一个节点一次。
--用法
使用GenericOptionsParser可以使用-file指定待分发的文件,-archieves复制存档文件(JAR文件,ZIP文件,tar文件盒gzipped tar文件),-libjars选项会把JAR文件添加到mapper和reducer任务的类路径中。文件可以存放在任何FS中,若未指定,则默认为本地的(非默认文件系统)。e.g.
public class MaxTemperatureByStationNameUsingDistributedCacheFile extends
Configured implements Tool {
static class StationTemperatureMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
parser.parse(value);
if (parser.isValidTemperature()) {
context.write(new Text(parser.getStationId()), new IntWritable(
parser.getAirTemperature()));
}
}
}
static class MaxTemperatureReducerWithStationLookup extends
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private NcdcStationMetadata metadata;
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
metadata = new NcdcStationMetadata(); metadata.initialize(new File("stations-fixed-width.txt"));
}
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String stationName = metadata.getStationName(key.toString());
int maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, value.get());
}
context.write(new Text(stationName), new IntWritable(maxValue));
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = JobBuilder.parseInputAndOutput(this, getConf(), args);
if (job == null) {
return -1;
}
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapperClass(StationTemperatureMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(MaxTemperatureReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(MaxTemperatureReducerWithStationLookup.class);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(
new MaxTemperatureByStationNameUsingDistributedCacheFile(),
args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
--工作机制
当用户启动一个作业,Hadoop将由-files和-archives选项所指定的文件复制到jobtracker的文件系统。接着,在任务运行之前,TaskTracker将文件从JobTracker的文件系统中复制到本地磁盘---缓存---这样Task就能访问这个文件。
TaskTracker为缓存中的文件维护一个计数器来统计这些文件的被使用情况。当任务即将运行时,针对该文件的计数器会自动增加1;当任务执行完毕,这个计数器会相应的减去1。当相关计数器为0的时,表明该文件没有被任何任务使用,可以从缓存中移除。
文件放在${mapred.local.dir}/taskTracker/archive,同时这些文件以符号链的方式指向任务的工作目录,对于用户不用细究。
缓存的大小配置
core-site.xml
<property>
<name>local.cache.size</name>
<value>10737418240</value>
<description>The limit on the size of cache you want to keep, set by default
to 10GB. This will act as a soft limit on the cache directory for out of band data.
</description>
</property>
5.MapReduce类库
Hadoop还为mapper和reducer提供了一个常用的函数库

6.参考资料
http://www.cnblogs.com/biyeymyhjob/archive/2012/08/12/2634252.html
Hadoop权威指南 |
|